Difference between DISBURSEMENT & REIMBURSEMENT
Disbursement (Payment)

Disbursement refers to the payment or expenditure of funds, typically made by a company, institution, or individual to another party, involving an outflow of money.
For example, a company or institution may make disbursements for:
- Employee salaries (e.g., monthly wages, bonuses)
- Office operational costs (e.g., rent, utilities, equipment purchases)
- Supplier payments (e.g., goods or services procurement)
- Project funding (e.g., research and development, marketing expenses)
- Grants / subsidies (e.g., government grants, corporate sponsorships)

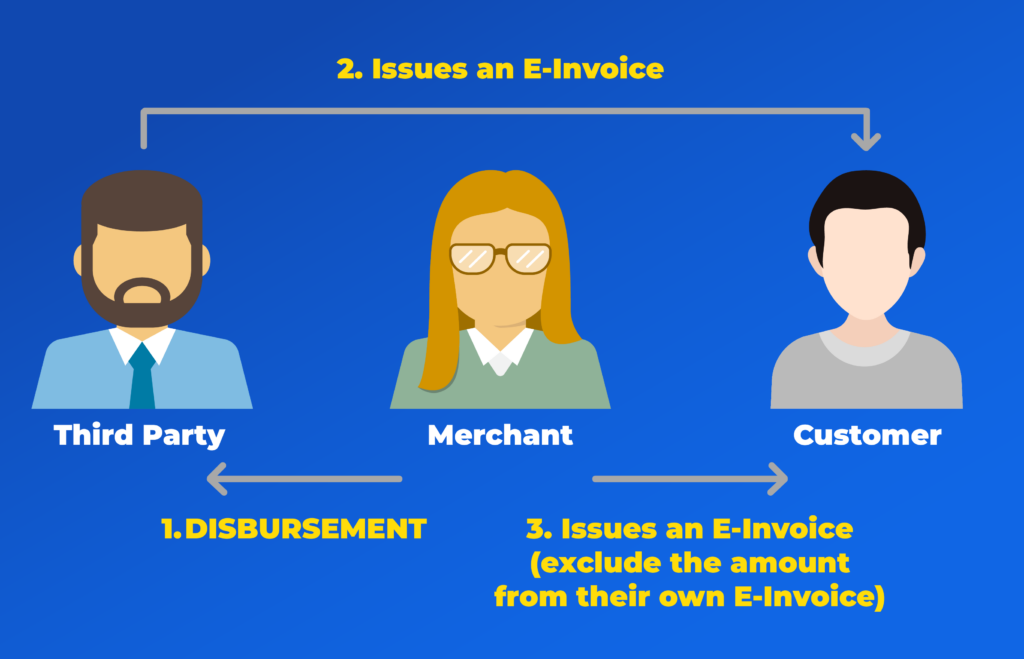
Special Case:
Merchant Pays on Behalf of the Customer
In some business scenarios, a merchant may advance payment on behalf of a customer but exclude the amount from their own E-Invoice. Instead, they provide a receipt and request the customer to reimburse the amount.
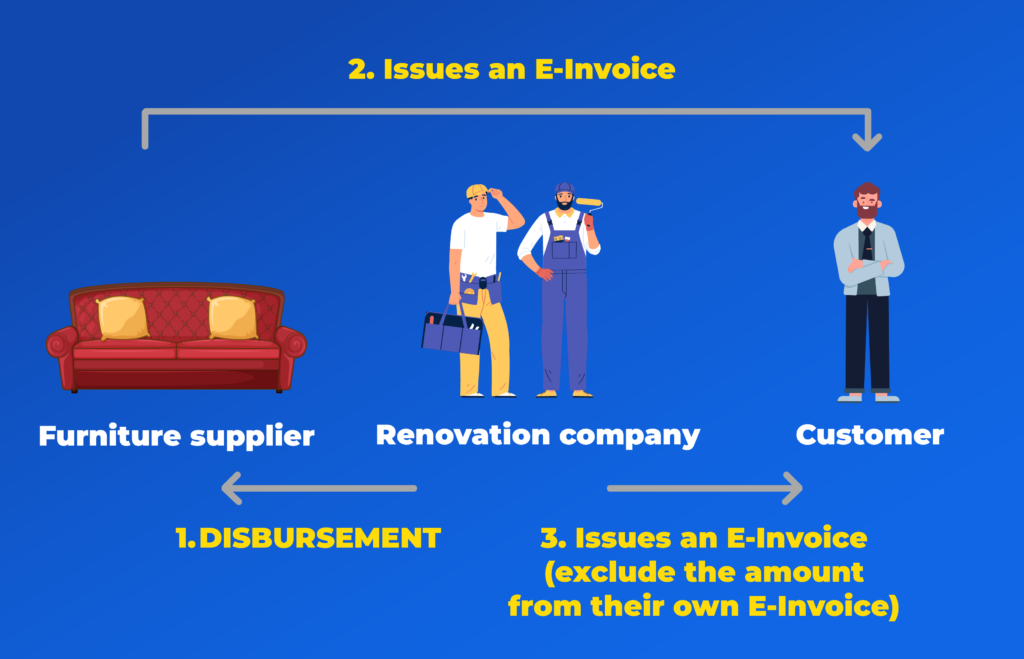
Example:
A customer orders custom furniture through a renovation company. The furniture supplier issues an E-Invoice directly to the customer, but the renovation company pays the amount on behalf of the customer. Later, the renovation company issues an E-Invoice to the customer (excluding the furniture cost), provides a receipt, and requests the customer to settle the amount.
Reimbursement (Repayment)

Reimbursement refers to the repayment or reimbursement of expenses that have already been paid. This typically occurs when an individual or organization initially covers a cost, and later, the responsible party reimburses them, involving a cash inflow to the payee.
For example, reimbursements may apply to:
- Employee out-of-pocket expenses (e.g., office supplies, travel, lodging, meals, client entertainment)
- Medical and healthcare expenses (e.g., doctor visits, medical check-ups, insurance claims)
- Training and education expenses (e.g., professional training, course fees, exam fees)

Special Case:
Merchant Pays First and Later Claims Reimbursement from the Customer
In some situations, a merchant may pay first and later include the expense in the E-Invoice for reimbursement.
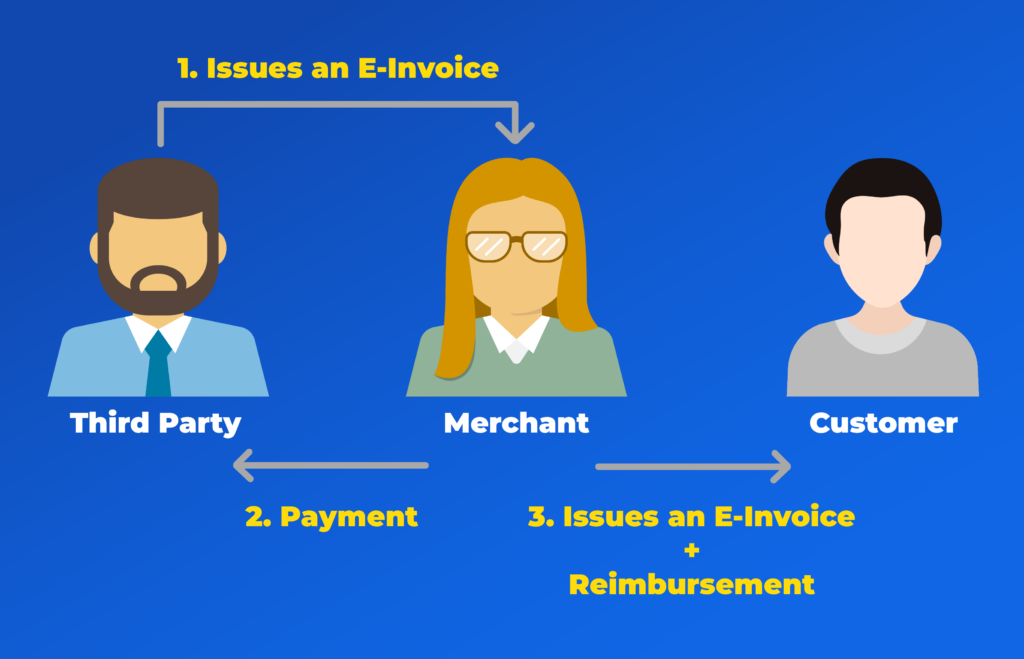
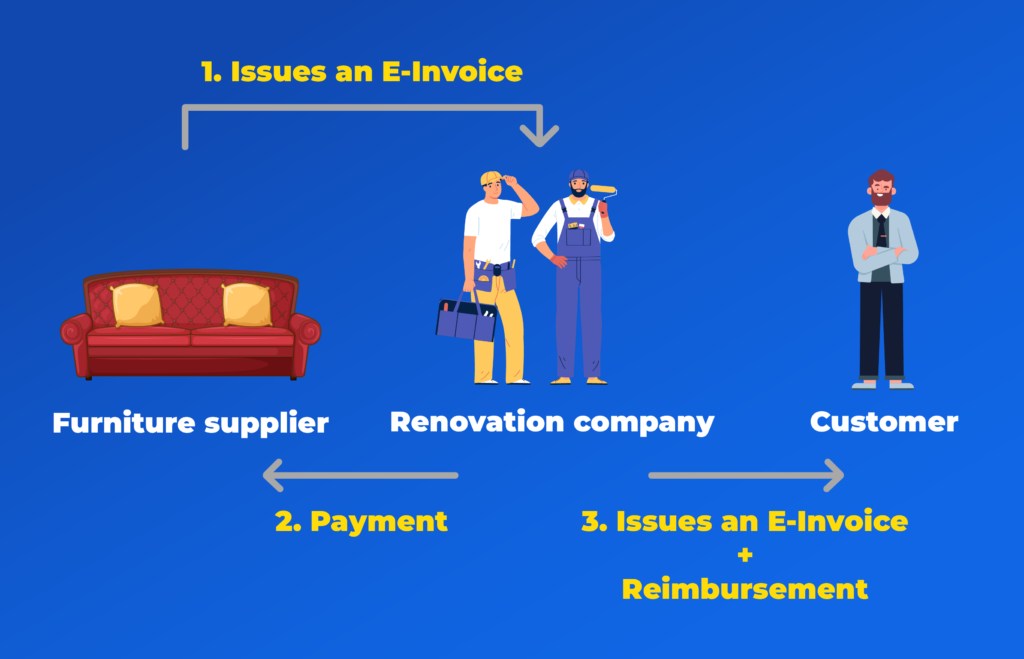
Example:
A renovation company orders furniture for a customer from a supplier. The furniture supplier issues an E-Invoice to the renovation company, which pays the amount upfront. Later, when invoicing the customer, the renovation company adds the furniture cost to the E-Invoice and requests reimbursement for the expense.